The Revised Cardiac Risk Index (RCRI) Calculator is a tool used to assess a patient's risk of cardiac complications during non-cardiac surgery. This calculator utilizes several clinical factors to stratify patients based on their likelihood of experiencing adverse cardiac events. The RCRI takes into account variables such as the patient's history of ischemic heart disease, heart failure, cerebrovascular disease, diabetes requiring insulin, renal insufficiency, and the type of surgery being performed. By evaluating these factors, healthcare providers can make informed decisions regarding perioperative management, including the need for additional cardiac evaluation or intervention. The RCRI Calculator is a valuable resource for improving patient safety and outcomes in surgical settings.
Patient Data Entry Guide
Step 1: Input Clinical Risk Factors
- High-Risk Surgery:
Yes(Intraperitoneal, intrathoracic, or vascular surgery).No(Other surgeries).- Example:
Yes
- History of Ischemic Heart Disease:
Yes(Prior MI, angina, or coronary revascularization).No.- Example:
No
- History of Congestive Heart Failure:
Yes(Prior CHF diagnosis or symptoms).No.- Example:
Yes
- History of Cerebrovascular Disease:
Yes(Prior stroke or TIA).No.- Example:
No
- Preoperative Insulin Treatment:
Yes(Diabetes requiring insulin).No.- Example:
No
- Preoperative Creatinine >2.0 mg/dL:
Yes(Serum creatinine ≥2.0 mg/dL).No.- Example:
Yes
Step 2: Input Symptoms
- Symptoms: Describe cardiac-related symptoms.
- Example:
Exertional dyspnea, chest discomfort
- Example:
Sample Diagnostic Report
RCRI Score Calculation
- Input Risk Factors:
- High-Risk Surgery: Yes (+1)
- Ischemic Heart Disease: No (0)
- Heart Failure: Yes (+1)
- Cerebrovascular Disease: No (0)
- Insulin Use: No (0)
- Creatinine >2.0 mg/dL: Yes (+1)
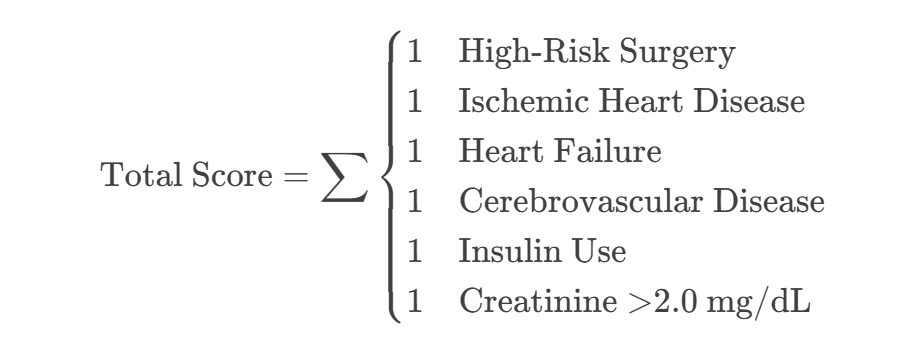
- Total RCRI Score:1+1+1=3 Points1+1+1=3 Points
Interpretation
- Risk Category: High (≥3 Points).
- Estimated Cardiac Complication Risk:
- Myocardial Infarction: ~11%.
- Cardiac Arrest: ~3%.
Symptom Correlation
- Exertional dyspnea suggests possible undiagnosed heart failure or ischemia.
Recommendations
- Preoperative Optimization:
- Consult cardiology for stress testing or echocardiography.
- Optimize CHF management (e.g., diuretics, beta-blockers).
- Intraoperative Monitoring:
- Invasive hemodynamic monitoring (e.g., arterial line).
- Postoperative Care:
- Troponin surveillance for 48 hours.
- Extended cardiac monitoring.
Key Considerations
- Risk Categories:
- 0 Points: Very Low Risk (0.4% complications).
- 1 Point: Low Risk (1.0%).
- 2 Points: Moderate Risk (2.4%).
- ≥3 Points: High Risk (5.4–11%).
- Limitations:
- Excludes emergency surgeries and specific populations (e.g., liver transplant).
- Less predictive for orthopedic or low-risk procedures.
- Adjunct Tools:
- Combine with METs assessment (functional capacity) for refined risk stratification.
Equations
RCRI Scoring:
Risk Stratification Table
| RCRI Score | Risk Category | Major Cardiac Complication Risk |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Very Low | 0.4% |
| 1 | Low | 1.0% |
| 2 | Moderate | 2.4% |
| ≥3 | High | 5.4–11% |
Final Diagnosis: Combines RCRI score and symptoms to guide preoperative interventions (e.g., defer surgery for unstable angina or initiate beta-blockers).
✅ Score Verification:
- Example: 3 risk factors → High-risk category with 5.4–11% complication risk.
Next Steps
- Perform ECG and echocardiogram.
- Optimize renal function preoperatively (e.g., hydration).
- Consider noninvasive stress testing if intermediate/high risk.

