The Fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) Index Calculator is a non-invasive tool used to assess the degree of liver fibrosis in individuals with liver disease. This calculator utilizes a simple formula that incorporates age, liver enzymes (AST and ALT), and platelet count to estimate the level of fibrosis.
Patient Data Entry Guide
Step 1: Input Laboratory Values
- AST (Aspartate Aminotransferase): Enter value + unit (U/L).
- Example: 48 U/L
- ALT (Alanine Aminotransferase): Enter value + unit (U/L).
- Example: 35 U/L
- Platelet Count: Enter value + unit (10⁹/L or cells/μL).
- Example: 150 x10⁹/L or 150,000 cells/μL
Step 2: Input Demographic Data
- Age: Enter age in years.
- Example: 52
- Sex: Specify Male/Female/Other.
- Example: Male
Step 3: Input Symptoms
- Symptoms: Describe symptoms or clinical concerns.
- Example: Fatigue, jaundice, abdominal distension
Sample Diagnostic Report
FIB-4 Index Calculation
- AST: 60 U/L | ALT: 40 U/L
- Platelets: 120 x10⁹/L
- Age: 50 years | Sex: Female
- Formula:
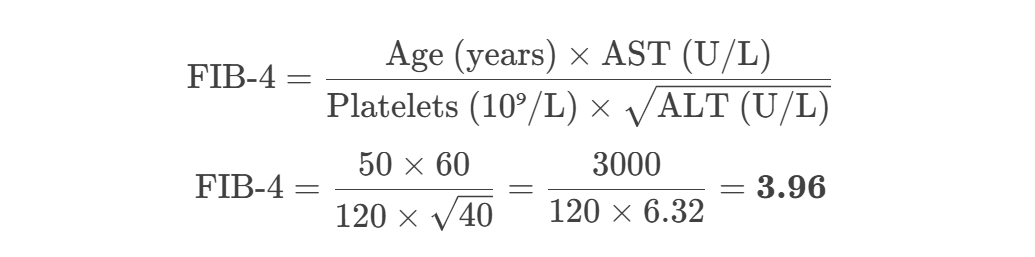
Interpretation
- FIB-4 Risk Stratification:
- <1.45: Low risk of advanced fibrosis.
- 1.45–3.25: Indeterminate (consider additional tests).
- >3.25: High risk of advanced fibrosis.
- Result: 3.96 (High risk of cirrhosis).
Symptom Correlation
- Jaundice and abdominal distension suggest decompensated liver disease.
Recommendations
- Liver Biopsy: Strongly recommended for staging fibrosis.
- Imaging: Perform transient elastography (FibroScan) or MRI elastography.
- Monitor for Complications: Screen for portal hypertension, varices, and HCC.
- Etiology-Specific Treatment:
- HCV: Direct-acting antivirals (DAAs).
- NAFLD: Lifestyle modification, weight loss.
Key Considerations
- Unit Conversions:
- Platelets (cells/μL → 10⁹/L): Divide by 1,000 (e.g., 150,000 cells/μL = 150 x10⁹/L).
- Limitations:
- Less accurate in patients with acute hepatitis, HIV coinfection, or thrombocytopenia from non-liver causes.
- Age Adjustment: Overestimates fibrosis in elderly patients (>65 years).
- Alternative Tools: Combine with APRI Score or NAFLD Fibrosis Score for improved accuracy.
Equation
FIB-4 Index Formula:
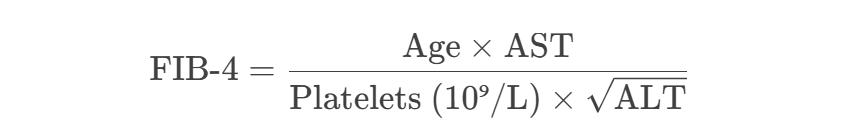
Risk Stratification Table
| FIB-4 Index | Risk Category | Clinical Action |
|---|---|---|
| <1.45 | Low | Monitor with routine labs/imaging |
| 1.45–3.25 | Indeterminate | Confirm with elastography or biopsy |
| >3.25 | High (Advanced Fibrosis) | Urgent biopsy and hepatology referral |
Final Diagnosis: Combines FIB-4 index, symptoms, and etiology to guide management (e.g., biopsy for HCV with FIB-4 >3.25 or lifestyle intervention for NAFLD).
✅ Formula Verification:
Example: Age=50, AST=60, ALT=40, Platelets=120 → FIB-4=3.96
Next Steps
- Assess viral load (HCV RNA, HBV DNA) if applicable.
- Exclude alcohol use or drug-induced liver injury.
- Initiate surveillance for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in high-risk patients.

